Special education teaching
Special education teaching
8 education terms
My name is Arianne, I am a student in education and this glossary will be for anyone who is interested in learning more about the field of Special Education Teaching (Special Ed.). It contains 8 terms, 7 of them being the main 7 learning disabilities. The definitions were fond on Walden University's website: waldenu.edu.
- Auditory processing disorder
- noun
- In auditory processing disorder (APD), patients have difficulty processing sounds. Individuals with APD may confuse the order of sounds or be unable to filter different sounds, like a teacher’s voice versus background noise. In APD, the brain misinterprets the information received and processed from the ear.
- Example: Olivia has APD, she has a hard time filtering different sounds.
- fr: trouble du traitement auditif

- Autism
- noun
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental disability; signs typically appear during early childhood and affect a persons ability to communicate, and interact with others. ASD is defined by a certain set of behaviors and is a spectrum condition that affects individuals differently and to varying degrees.
- Example: My friend Paul was diagnosed with Autism spectrum disorder when he was younger.
- fr: Autisme

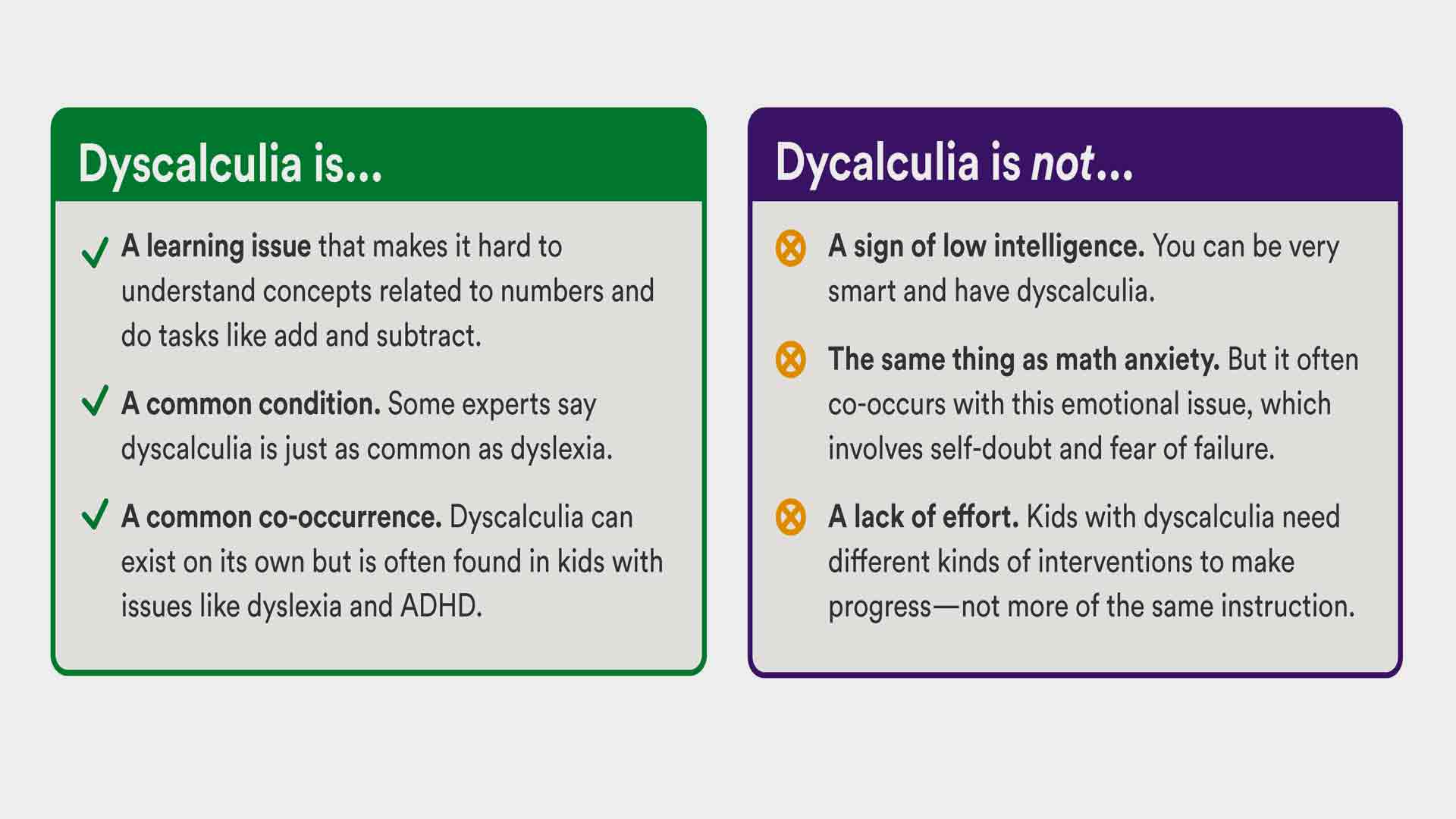
- Dyscalculia
- noun
- Dyscalculia encompasses learning disabilities related to mathematical calculations. Individuals with dyscalculia struggle with math concepts, numbers, and reasoning. Sometimes referred to as having “math dyslexia,” individuals might have difficulty reading clocks to tell time, counting money, identifying patterns, remembering math facts, and solving mental math.
- Example: George has dyscalculia, they have difficulty reading the clock to tell time.
- fr: Dyscalculie
- Dysgraphia
- noun
- People with dysgraphia have trouble converting their thoughts into writing or drawing. Poor handwriting is a hallmark of dysgraphia but is far from the only symptom. Sufferers struggle to translate their thoughts into writing, whether in spelling, grammar, vocabulary, critical thinking, or memory. Individuals with dysgraphia may exhibit difficulty with letter spacing, poor motor planning and spatial awareness, and trouble thinking and writing simultaneously.
- Example: Julia has dysgraphia, they have trouble with spacing their letters.
- fr: Dysgraphie

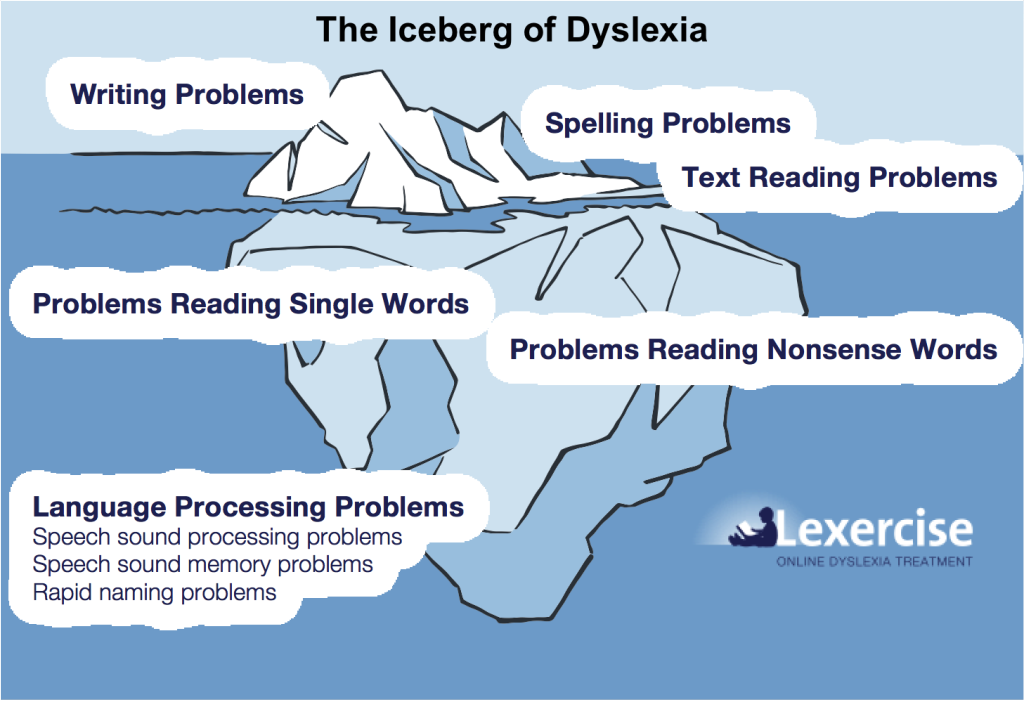
- Dyslexia
- noun
- Dyslexia is a language processing disorder that impacts reading, writing, and comprehension. People who have dyslexia may exhibit difficulty decoding words or with phonemic awareness, identifying individual sounds within words. Dyslexia often goes diagnosed for many years and often results in trouble with reading, grammar, reading comprehension, and other language skills.
- Example: Lea has dyslexia, which makes it difficult for her to read and write.
- fr: Dyslexie
- Language processing disorder
- noun
- A subset of auditory processing disorder, language processing disorder arises when an individual has specific challenges in processing spoken language, impacting both receptive and expressive language. According to the Learning Disabilities Association of America, in language processing disorder, “there is difficulty attaching meaning to sound groups that form words, sentences, and stories.”
- Example: Mikayla has LPD, she often has incomplete thoughts or sentences.
- fr: trouble du traitement du langage

- Nonverbal learning disabilities
- noun
- While it may sound like nonverbal learning disabilities (NVLD) relate to an individual’s inability to speak, it actually refers to difficulties in decoding nonverbal behaviors or social cues. NVLD sufferers struggle with understanding body language, facial expressions and tone of voice, or the nonverbal aspects of communication.
- Example: Arielle has NVLD, she has a difficult time with social clues, such as reading someone's body language or facial expressions.
- fr: troubles d’apprentissage non verbaux

- visual perceptual/visual motor deficit
- noun
- Individuals with visual perceptual/visual motor deficit exhibit poor hand-eye coordination, often lose their places when reading, and have difficulty with pencils, crayons, glue, scissors, and other fine motor activities. They may also confuse similar looking letters, have trouble navigating their surroundings, or demonstrate unusual eye activity when reading or completing assignments.
- Example: Anisha has visual motor deficit, she often lose her place when reading.
- fr: Déficit sensivo-moteur
















